Intro
Traceroute is a network diagnostic tool for determining the network path to the destination IP from your computer. Most modern operating systems should have this command or something similar. On UNIX-like systems like FreeBSD, macOS and Linux, this tool exists as a command line program. On the other hand, Windows has a similarly named tool called tracert.
Doing a traceroute to google.com in Windows
Since this tool is a command line program, we need to open a Command Prompt first.
- Press the Windows button, type cmd to search for the Command Prompt.
- Once you see the Command Prompt appear, click on it.
- Inside the Command Prompt, type tracert google.com and press Enter on your keyboard.
You should see something like the below as your tracert result.
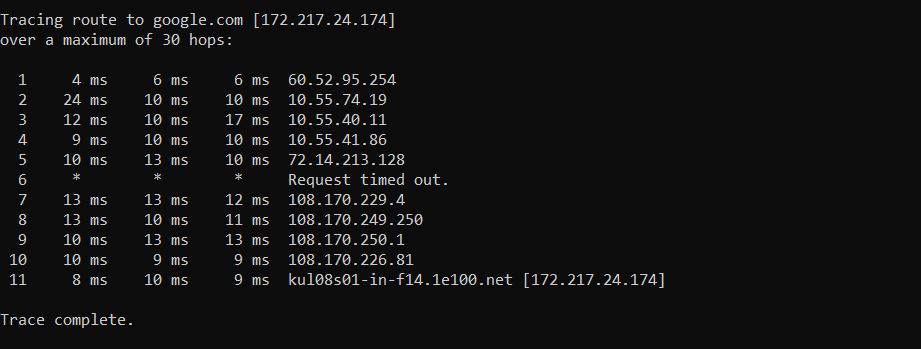
In the above image, you can see a few columns of data.
The first column is the hop number which is just the number of the hop along the route.
The next 3 columns are referring to the same thing, which is the round trip time (RTT) taken for your packet to reach that point and return to your computer. 3 separate signal packets are sent to give you an idea of the consistency of the route.
The final column is the IP address or hostname for the router.
Doing a traceroute to google.com in Linux
Since this tool is a command line program, if you’re running Linux with Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) then you need to launch a terminal. Otherwise you should already be in a terminal.
At the command prompt, type traceroute google.com and press Enter on your keyboard.
* Note the different tool name.
You should see something like the below as your traceroute result.
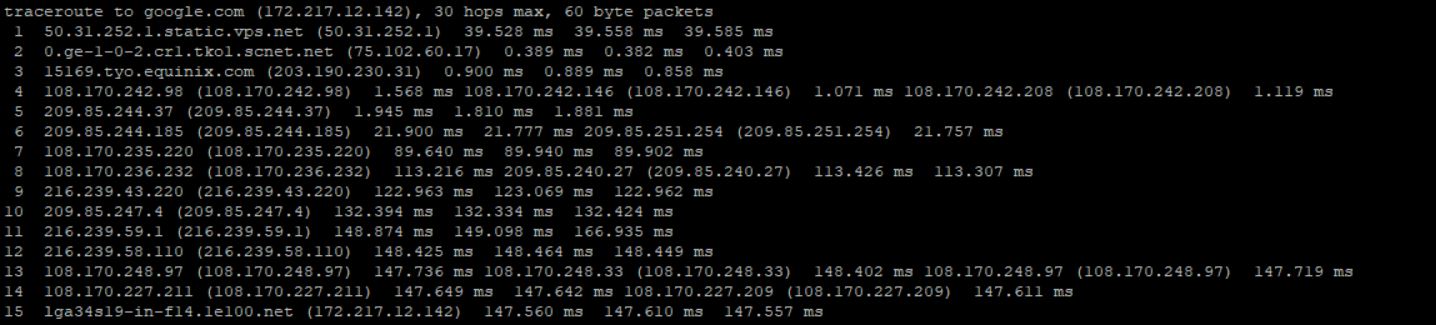
In the above image, you’ll notice that the output is slightly different from the earlier one.
First, you see the hop number which is just the number of the hop along the route.
Next is the router hostname and IP address along with the 3 RTT numbers.
You may also see a different IP address appear next to the 2nd or 3rd RTT number. This just indicates that this particular signal went along a slightly different route during that hop.