
IP2Location MySQL docker simplifies the efforts to setup up the geolocation database for IP lookup. In this tutorial, we are going to demonstrate how to set up the IP2Location MySQL docker and how to use it in a Debian container. And, we are going to use the docker network for the connection.
Setup IP2Location MySQL Instance
We assume that you have the docker environment installed before you continue reading this article. First of all, download ip2location/mysql image from docker hub using the below command:
sudo docker pull ip2location/mysql
You should see the below screenshot if you had successfully downloaded the ip2location/mysql image.
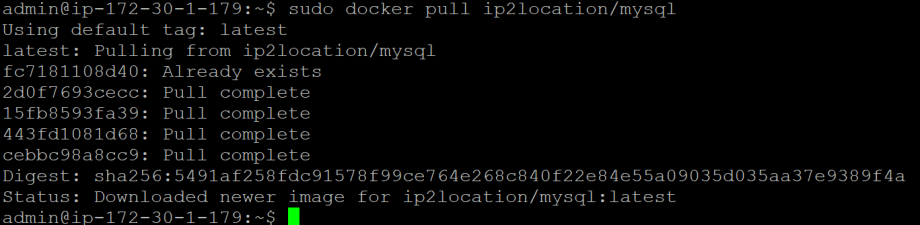
In addition, you can also check using sudo docker images command. You should see the ip2location/mysql repository name appearing in the list. Next, you can create the container and set up the geolocation database. Before doing so, you will need a download token. If you are a client of ip2location.com or lite.ip2location.com, you can login to the account area to retrieve the download token. If you are not, you can subscribe for a free LITE account at https://lite.ip2location.com to get the download token.
Once you have the token ready, you can initiate the below command for the installation:
docker run --name ip2location -d -e TOKEN={DOWNLOAD_TOKEN} -e CODE={DOWNLOAD_CODE} ip2location/mysql
whereby, the {DOWNLOAD_TOKEN} is the ASCII string that you retrieved from your account area, and the {CODE} is the database that you would like to install. The CODE information can also be located in your account area. For example, if you are going to use IP2LOCATION DB3 LITE and your token is 123456. Below is the example of the command:
docker run --name ip2location -d -e TOKEN=123456 -e CODE=DB3LITE ip2location/mysql
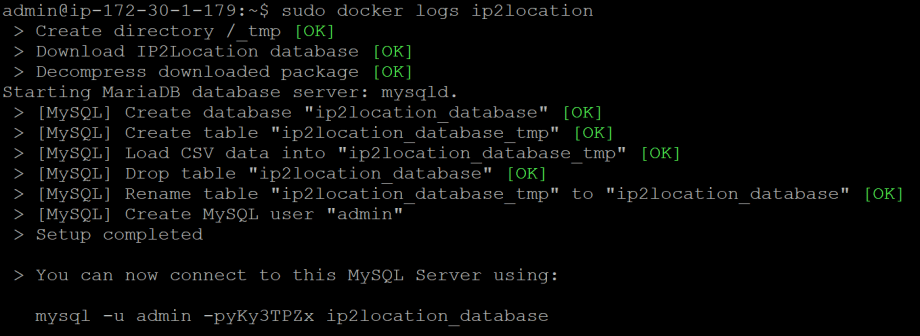
Hit the enter button to run the above command. Then, you can invoke sudo docker logs ip2locationcommand to check the database setup progress. If the database was successfully setup, you should see the below screenshot:Please note that MySQL password will be randomly assigned during the database installation. You must record the password somewhere as you will need it for the subsequent connection. In the above example, the password would be yKy3TPZx and the username is always admin.
You are now done with the IP2Location MySQL setup. You may also check if the ip2location instance is running by issuing the following command.
sudo docker ps
Setup Debian container
We will now proceed to set up the Debian container. You can skip this step if you already have the container ready. Run the below command to download the Debian image.
sudo docker pull debian
Please note that we will use the latest version of Debian in this article. However, if you want, you may specify the Debian version that you want to download. For the purpose of this write up, we are using Debian 10, buster.
After the downloading is done, run the below command to start the container.
sudo docker run --name debian-test -it debian bin/bash
You should now be in the container environment if you had successfully created and ran the container. You will notice the below screenshot:
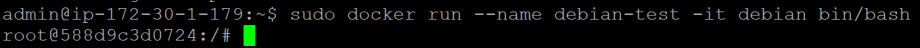
Click on CTRL+Pfollowed by CTRL+Qto detach from the container. Please do not type the exit command as it will shut down the container, as we still need to container to be up and running for the testing.
How to use IP2Location MySQL database in Debian container
You have both debian-test container and ip2location created and ran, but they are not communicating with each other. You will need to create a network to connect both of them. To do so, you need to create a simple bridge network as below:
sudo docker network create simple-network
Connect both container into the same network using the below command
sudo docker network connect simple-network ip2location sudo docker network connect simple-network debian-test
Now, you can go back to debian-test container using the below command so that you can test the connection.
sudo docker attach debian-test
Try pinging for ip2location, and you should see the response successfully. Now, the container is in the same network and capable to see each other. Next, you can issue the below mysql command to test the IP lookup. If everything is set up correctly, you should see the below response.
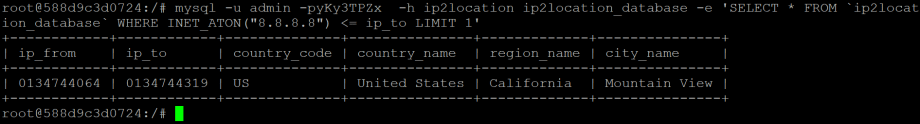
The above tutorial is just a simple guide to access the IP2Location MySQL container. In fact, you can run a PHP, Ruby or other container to implement any geolocation solution you want.

