Intro
Dart is a client-optimized, object-oriented programming language developed by Google for building fast apps on multiple platforms, including mobile, desktop, web, and server-side applications. It is best known as the language behind Flutter, Google’s UI toolkit for creating cross-platform applications. Dart features C-style syntax, modern capabilities like null safety and async-await, and the ability to compile to different machine code and JavaScript targets.
In this article, we’ll show how to use the IP2Location Dart package in a Dart command line (CLI) project to easily query the IP2Location BIN files to retrieve geolocation data for an IPv4 or IPv6 address. Our example will be using Debian 13 so some of the steps will be specific for that platform.
Pre-requisites
First, install Dart if you don’t have it installed on your system. Refer to https://dart.dev/get-dart for the installation steps specific to your system. In addition to that, you’ll also need the IP2Location DB26 BIN database files that contains the geolocation data. You can download the BIN file from either of the below:
Commercial BIN files: https://www.ip2location.com
Free LITE BIN files: https://lite.ip2location.com
Download the zipped file and extract the BIN file to a folder of your choosing. For our case, we are storing the BIN file path as /home/admin/data/IP2LOCATION-DB26.IPV6.BIN so that’s what we’ll use later.
Create a new Dart console project
Navigate to the folder where you want to create the new project. In our case, it’s dartarticle.
Next, run the below command to create an initial Dart console project.
dart create -t console ip2location_cli
Then, navigate to the newly created folder.
cd ip2location_cli
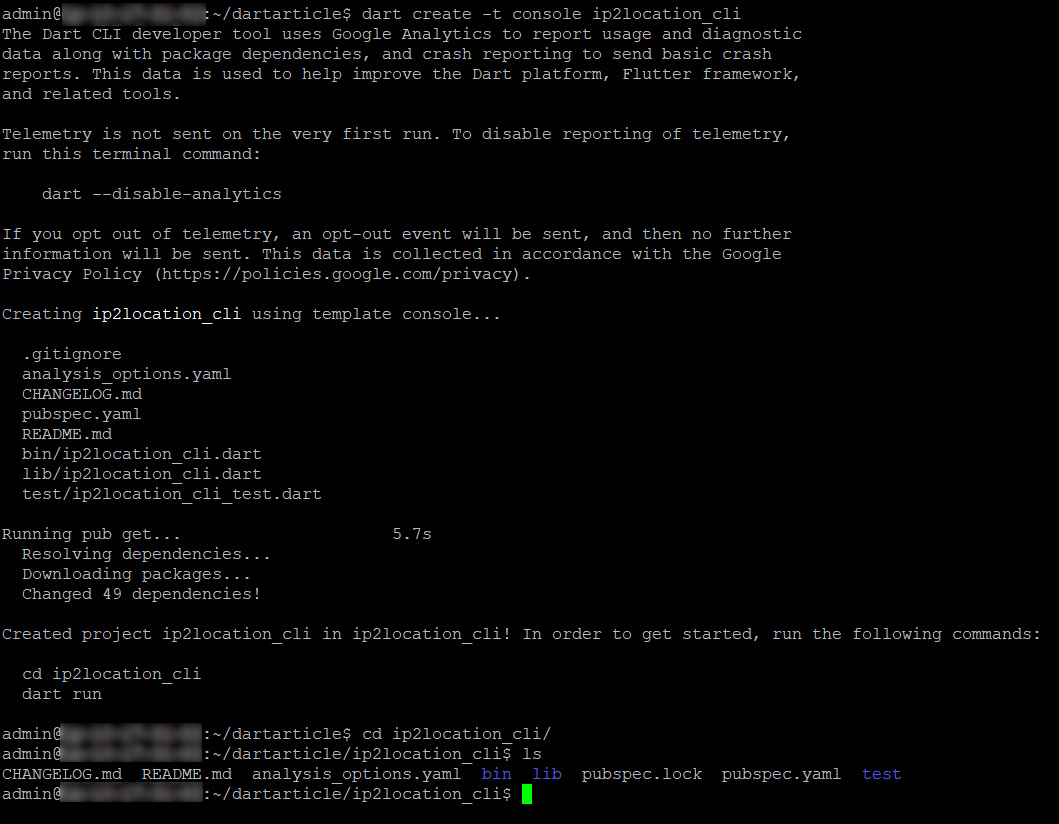
This creates a small CLI app with bin/ip2location_cli.dart as the entrypoint.
Include the IP2Location Dart as a dependency
Check for the latest version of the IP2Location Dart package at https://pub.dev/packages/ip2location/install and modify the code below for that version. We are also using the args package for specifying the command line parameters.
Edit the pubspec.yaml and add the below under the dependencies section:
ip2location: ^8.1.0
args: ^2.7.0
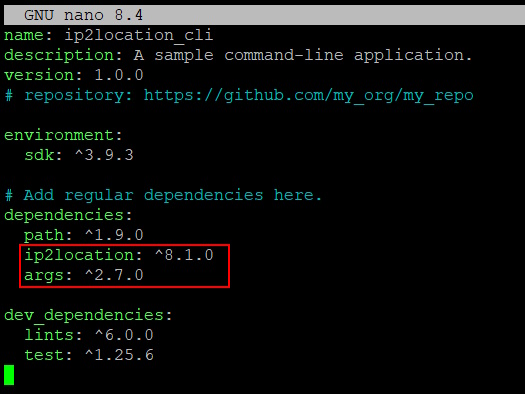
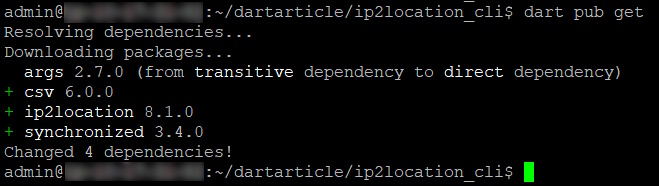
Save the file and run the command below to fetch the dependencies.
dart pub get
Implement the command line codes
Edit bin/ip2location_cli.dart and replace the existing codes with the codes below.
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:args/args.dart';
import 'package:ip2location/ip2location.dart';
void main(List<String> arguments) async {
final parser = ArgParser()
..addOption('db', abbr: 'd', help: 'Path to IP2Location BIN database');
final results = parser.parse(arguments);
if (results.rest.isEmpty) {
print('Usage: ip2location_cli <IP> -d <DB_PATH>');
exit(1);
}
final ip = results.rest[0];
final dbFile = results['db'] ?? 'IP2LOCATION-LITE-DB1.BIN';
IP2Location ipl = IP2Location(databasePath: dbFile);
try {
final result = await ipl.getAll(ip);
print('IP Address: ${ip}');
print('countryShort: ${result.countryShort}');
print('countryLong: ${result.countryLong}');
print('region: ${result.region}');
print('city: ${result.city}');
print('isp: ${result.isp}');
print('latitude: ${result.latitude?.toStringAsFixed(6)}');
print('longitude: ${result.longitude?.toStringAsFixed(6)}');
print('domain: ${result.domain}');
print('zipCode: ${result.zipCode}');
print('netSpeed: ${result.netSpeed}');
print('timeZone: ${result.timeZone}');
print('iddCode: ${result.iddCode}');
print('areaCode: ${result.areaCode}');
print('weatherStationCode: ${result.weatherStationCode}');
print('weatherStationName: ${result.weatherStationName}');
print('mcc: ${result.mcc}');
print('mnc: ${result.mnc}');
print('mobileBrand: ${result.mobileBrand}');
print('elevation: ${result.elevation}');
print('usageType: ${result.usageType}');
print('addressType: ${result.addressType}');
print('category: ${result.category}');
print('district: ${result.district}');
print('asn: ${result.asn}');
print('asName: ${result.asName}');
print('asDomain: ${result.asDomain}');
print('asUsageType: ${result.asUsageType}');
print('asCIDR: ${result.asCIDR}');
} catch (e) {
stderr.writeln('Error looking up IP: $e');
exit(1);
}
}
The code accepts the first parameter as the IP address to query for geolocation. User can also optionally specify the location of the BIN file using the -d flag. If not specified, the code will look for IP2LOCATION-LITE-DB1.BIN instead.
Test the code
Let’s test the code and make sure everything is working.
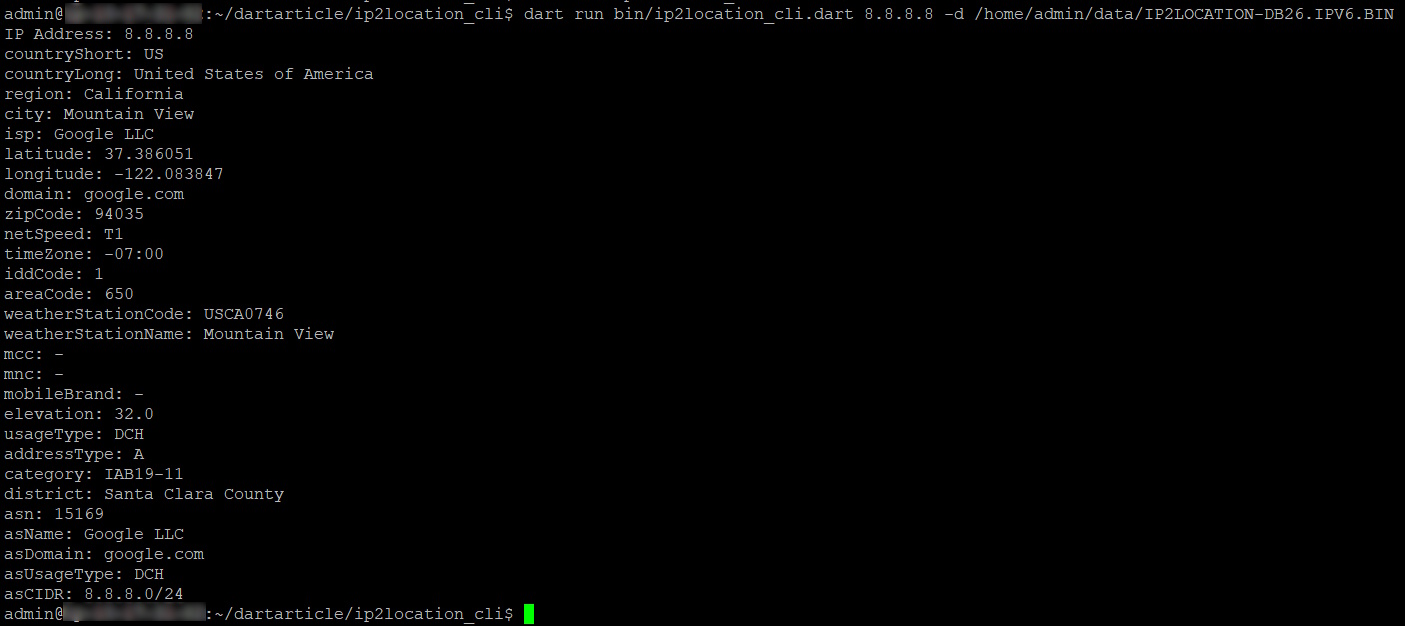
Use the command below to test the code.
dart run bin/ip2location_cli.dart 8.8.8.8 -d /home/admin/data/IP2LOCATION-DB26.IPV6.BIN
You’ll see the results below.
IP Address: 8.8.8.8 countryShort: US countryLong: United States of America region: California city: Mountain View isp: Google LLC latitude: 37.386051 longitude: -122.083847 domain: google.com zipCode: 94035 netSpeed: T1 timeZone: -07:00 iddCode: 1 areaCode: 650 weatherStationCode: USCA0746 weatherStationName: Mountain View mcc: - mnc: - mobileBrand: - elevation: 32.0 usageType: DCH addressType: A category: IAB19-11 district: Santa Clara County asn: 15169 asName: Google LLC asDomain: google.com asUsageType: DCH asCIDR: 8.8.8.0/24
Compile into executable binary
To make it easier to distribute to other Linux users, we can go an extra step and compile it into a native executable binary.
Run the below command in the root of your project folder to compile the code.
dart compile exe bin/ip2location_cli.dart -o ip2location_cli

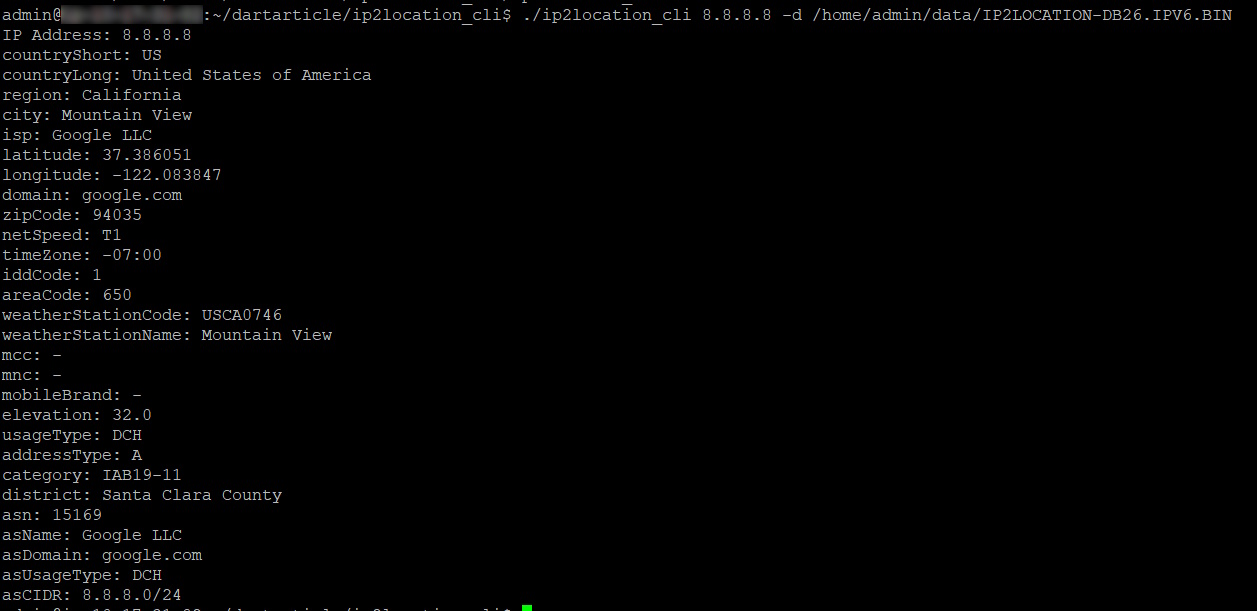
Run the executable to get your geolocation results
Run the executable to get your geolocation similar to our testing command, with just a slight difference. You should see the same results.
./ip2location_cli 8.8.8.8 -d /home/admin/data/IP2LOCATION-DB26.IPV6.BIN
Conclusion
It is very straightforward to call the IP2Location Dart package in your code as we’ve shown above. So, no reason why you can’t include geolocation functionality into your Dart programs or apps. This will seriously enhance the functionality of your codes.
THE POWER OF IP GEOLOCATION
Find a solution that fits.
